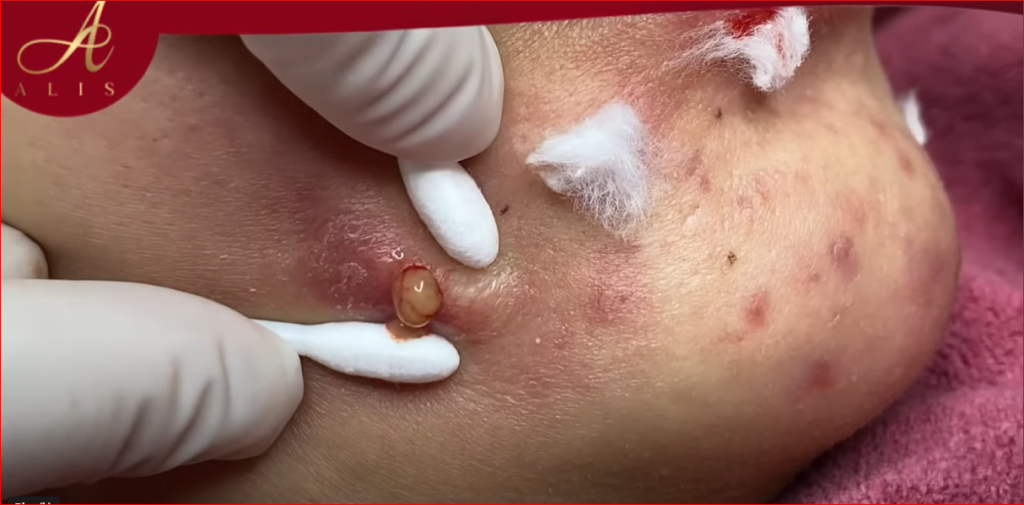
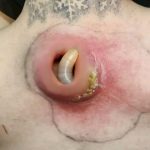
Acne treatment depends on the severity and type of acne (e.g., blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, cysts). Here’s a general overview of effective acne treatments:
✅ Basic Skincare Routine (for mild acne)
-
Cleanser: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser twice a day.
-
Moisturizer: Even oily skin needs moisture. Use an oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizer.
-
Sunscreen: Choose a non-comedogenic sunscreen daily.
🔬 Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
-
Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills bacteria and reduces inflammation.
-
Salicylic Acid: Helps unclog pores and exfoliates skin.
-
Adapalene (Differin): A retinoid that helps prevent clogged pores and reduces inflammation.
💊 Prescription Treatments (for moderate to severe acne)
-
Topical Retinoids: Like tretinoin or adapalene.
-
Topical Antibiotics: Clindamycin or erythromycin, often combined with benzoyl peroxide.
-
Oral Antibiotics: Doxycycline, minocycline, etc., used short-term.
-
Hormonal Treatments: Birth control pills or spironolactone (for females).
-
Isotretinoin (Accutane): A powerful treatment for severe, resistant acne.
🧴 Lifestyle Tips
-
Don’t pick or squeeze pimples.
-
Wash pillowcases regularly.
-
Avoid touching your face.
-
Use non-comedogenic makeup and skincare products.
🧬 Understanding Acne
Acne vulgaris is a common skin condition resulting from clogged pores due to excess sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria. It manifests in various forms:Byrdie
-
Comedonal Acne: Characterized by blackheads and whiteheads.
-
Inflammatory Acne: Includes papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
-
Hormonal Acne: Often linked to hormonal fluctuations, such as during menstruation or pregnancy.
🧴 Topical Treatments
1. Benzoyl Peroxide
-
Mechanism: Kills Propionibacterium acnes, the bacteria associated with acne.
-
Usage: Available over-the-counter in concentrations of 2.5%, 5%, and 10%.
-
Considerations: May cause dryness or irritation; start with a lower concentration. PMC
2. Retinoids (Vitamin A Derivatives)
-
Examples: Tretinoin, adapalene, tazarotene.
-
Benefits: Promote cell turnover, preventing clogged pores.
-
Usage: Apply in the evening; avoid combining with benzoyl peroxide due to potential irritation. Vogue+1Mayo Clinic+1Mayo Clinic
3. Topical Antibiotics
-
Examples: Clindamycin, erythromycin.
-
Usage: Often combined with benzoyl peroxide to reduce bacterial resistance.
-
Considerations: Not recommended as monotherapy; should be used in combination. AAFPAAFP
4. Azelaic Acid
-
Mechanism: Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Usage: Applied twice daily; suitable for individuals with sensitive skin.
💊 Oral Treatments
1. Oral Antibiotics
-
Examples: Doxycycline, minocycline.
-
Usage: Prescribed for moderate to severe acne; typically combined with topical treatments.
-
Considerations: Use for the shortest duration to minimize antibiotic resistance. Mayo Clinic
2. Combined Oral Contraceptives
-
Mechanism: Regulate hormones that can trigger acne.
-
Usage: Approved for use in females; may take several months to show effects.
3. Isotretinoin (Accutane)
-
Indication: Reserved for severe, cystic acne unresponsive to other treatments.
-
Considerations: Requires close monitoring due to potential side effects. Mayo Clinic
🌿 Lifestyle and Preventive Measures
-
Avoid Picking or Squeezing Pimples: Can lead to scarring and worsen inflammation.
-
Regularly Wash Pillowcases and Towels: Helps reduce bacterial buildup.
-
Use Non-Comedogenic Products: Ensure skincare and makeup products do not clog pores.
-
Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine: Consistency is key in managing acne.Vogue+1theaustralian.com.au+1
🩺 Professional Treatments
-
Light and Laser Therapies: Target bacteria and reduce inflammation.
-
Chemical Peels: Utilize acids like salicylic or glycolic acid to exfoliate the skin.
-
Steroid Injections: Administered for large cysts to reduce inflammation.
📌 Summary
Effective acne treatment involves a combination of topical and, if necessary, oral therapies tailored to the individual’s acne type and severity. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.