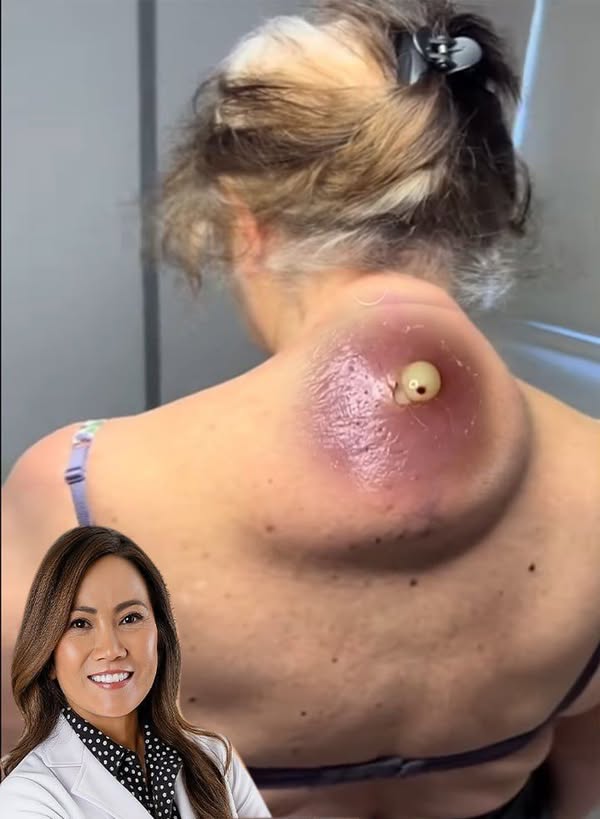
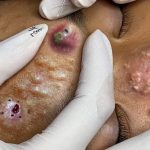
Big cyst removal (like sebaceous, epidermoid, or pilar cysts) should be done carefully to avoid infection, recurrence, or scarring. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how large cysts are removed, including home care, medical procedures, and when to seek help.
🏠 What Not to Do at Home
-
❌ Don’t squeeze or pop a large cyst — it can rupture internally, causing inflammation or infection.
-
❌ Don’t cut it yourself — this increases risk of scarring and serious infection.
🧑⚕️ Medical Removal of a Large Cyst (Office-Based Surgery)
1. Evaluation
-
The doctor assesses the cyst’s size, depth, location, and whether it’s infected.
-
If infected, they may delay surgery and start antibiotics first.
2. Minor Surgical Procedure (Most Common Approach)
Step-by-Step:
-
Local Anesthesia
-
Lidocaine is injected around the cyst to numb the area.
-
-
Incision
-
A small cut is made over the cyst.
-
-
Drainage (if necessary)
-
If the cyst is inflamed or filled with pus, the contents may be drained first.
-
-
Cyst Wall (Sac) Removal
-
The doctor carefully dissects and removes the entire cyst capsule (sac). This is crucial to prevent recurrence.
-
-
Closure
-
The incision may be closed with dissolvable or external stitches.
-
If infected, it may be left open to drain, packed with gauze, and closed later.
-
-
Bandage + Aftercare Instructions
-
Keep it clean, dry, and avoid strenuous activity for several days.
-
📚 Reference: Mayo Clinic – Cyst removal
3. Types of Cysts Commonly Removed
| Type | Common Location | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Epidermoid | Face, neck, trunk | Firm, slow-growing, often has a central pore |
| Sebaceous | Scalp, back, face | Oily content, from blocked sebaceous gland |
| Pilar (Trichilemmal) | Scalp | Often multiple, from hair follicles |
⚠️ When to See a Doctor
-
Cyst is large, painful, or growing rapidly
-
Infected (red, warm, pus, foul odor)
-
Recurs after past removal
-
Located on face, genitals, or joints
🩹 Aftercare Tips
-
Clean with saline or gentle soap
-
Apply antibiotic ointment if advised
-
Avoid picking or touching the wound
-
Return for stitch removal (if non-absorbable)
🏥 Special Cases: Cyst Bursting or Abscess
-
If the cyst bursts, it often becomes inflamed or infected.
-
Doctors may perform an I&D (incision and drainage) and remove the sac later after inflammation subsides.
Would you like a visual diagram of the procedure or a list of clinics near you that perform cyst removals?




Certainly! Here’s a detailed overview of medical procedures for removing large cysts, particularly epidermoid cysts, based on current medical practices and guidelines.
🧑⚕️ Medical Procedures for Large Cyst Removal
1. Minimal Excision Technique
-
Overview: This technique involves making a small 2–3 mm incision over the cyst, expressing the cyst contents, and then extracting the cyst wall through the opening. It’s effective for non-inflamed, uncomplicated cysts and minimizes scarring. AAFP+1theresapulsedermatology.com+1
-
Procedure:
-
Clean the area with antiseptic.
-
Administer local anesthesia (e.g., lidocaine).
-
Make a small incision over the cyst.
-
Express the cyst contents.
-
Remove the cyst wall.
-
Apply antibiotic ointment and cover with a sterile dressing.AAFP+3Healthline+3theresapulsedermatology.com+3staianoplasticsurgery.co.uk+5theresapulsedermatology.com+5Verywell Health+5
-
-
Advantages:
-
Minimal scarring.
-
Quick recovery.
-
Suitable for non-inflamed cysts.Healthline
-
-
Considerations:
-
Not suitable for inflamed or infected cysts.
-
Requires precision to ensure complete removal and prevent recurrence.
-
2. Incision and Drainage (I&D)
-
Overview: This is a quick procedure where a small incision is made to drain the cyst contents. It’s often used for infected cysts to relieve symptoms but may not prevent recurrence. Healthline
-
Procedure:
-
Clean the area with antiseptic.
-
Administer local anesthesia.
-
Make a small incision to drain the cyst.
-
Apply antibiotic ointment and cover with a sterile dressing.Healthline
-
-
Advantages:
-
Quick relief of symptoms.
-
Minimal scarring.
-
-
Considerations:
-
Higher risk of recurrence.
-
May not be suitable for large or deep cysts.
-
3. Marsupialization
-
Overview: This technique involves creating a continuous opening between the cyst and the skin surface, allowing it to drain freely. It’s used for cysts that are difficult to remove entirely or when complete excision isn’t feasible. Wikipedia
-
Procedure:
-
Clean the area with antiseptic.
-
Administer local anesthesia.
-
Make an incision to open the cyst.
-
Suture the edges of the cyst to the skin to form a continuous opening.
-
Apply antibiotic ointment and cover with a sterile dressing.Wikipedia
-
-
Advantages:
-
Useful for cysts that are difficult to remove entirely.
-
Prevents recurrence by allowing continuous drainage.
-
-
Considerations:
-
May require longer healing time.
-
Not suitable for all types of cysts.
-
🩹 Aftercare and Recovery
-
Wound Care:
-
Keep the area clean and dry.
-
Apply antibiotic ointment as prescribed.
-
Cover with a sterile dressing and change it regularly.
-
-
Activity Restrictions:
-
Avoid strenuous activities that could stress the wound.
-
Follow your healthcare provider’s advice on when to resume normal activities.AAFP+1AAFP+1
-
-
Follow-Up:
-
Attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing.
-
Contact your healthcare provider if you notice signs of infection (e.g., increased redness, swelling, or pus).
-