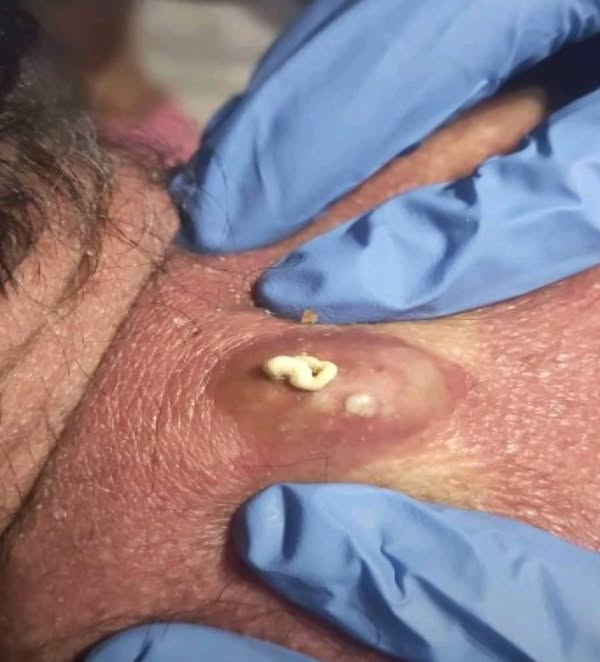
Removing a small lump or cyst depends on its type, location, cause, and whether it’s causing problems. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how doctors typically remove small lumps or cysts, especially those on the skin, breast, or under the skin.
🧼 How Small Lumps or Cysts Are Removed
🔍 Step 1: Diagnosis
A doctor first determines what the lump is:
-
Cyst: A fluid-filled sac (common ones: sebaceous, epidermoid, ganglion, breast cyst)
-
Lipoma: A fatty lump under the skin
-
Other masses: May need imaging (ultrasound, MRI) or biopsy
🛠 Step 2: Removal Options
1. Simple Excision (Minor Surgery)
-
Where: In a clinic or outpatient setting
-
How it works:
-
Local anesthetic (numbs the area)
-
A small cut is made over the cyst/lump
-
The entire cyst is removed, including its capsule (to prevent recurrence)
-
The area is stitched and bandaged
-
-
Time: ~20–40 minutes
-
Recovery: Minimal; stitches removed in ~7–10 days
2. Needle Aspiration
-
Used for: Fluid-filled cysts (e.g., breast cysts, ganglion cysts)
-
How it works:
-
A sterile needle is used to draw out the fluid
-
May be guided by ultrasound
-
Not a permanent solution (cysts may refill)
-
-
Recovery: Immediate, minimal discomfort
3. Drainage with Minor Incision
-
Used when: The cyst is infected or inflamed (abscess)
-
How it works:
-
Area is numbed
-
Small cut is made to drain pus/fluid
-
May be left open to heal naturally or packed with gauze
-
-
Recovery: Daily cleaning, healing in days to weeks
4. Laser or Electrosurgical Removal
-
Used for: Superficial skin cysts or cosmetic reasons
-
Less invasive and minimal scarring
📋 Aftercare
-
Keep the area clean and dry
-
Antibiotics may be given if infection risk is high
-
Watch for signs of infection (redness, swelling, fever)
🚩 When Removal Is Needed
You should see a doctor if the lump/cyst:
-
Grows in size
-
Becomes painful or red
-
Leaks fluid
-
Interferes with movement
-
Is cosmetically bothersome
-
Has uncertain cause (may need biopsy)
🧼 Understanding Small Lumps and Cysts
Small lumps or cysts are typically benign (non-cancerous) growths that can appear under the skin. Common types include:
-
Sebaceous cysts (epidermoid cysts): Filled with keratin and often found on the face, neck, or torso.
-
Ganglion cysts: Fluid-filled sacs commonly located near joints or tendons, especially in the wrist or hand.
-
Myxoid cysts: Fluid-filled lumps near the nail bed of fingers or toes, often associated with osteoarthritis.
🛠 Treatment Options for Removal
1. Surgical Excision
Procedure:
-
Preparation: The area is cleaned, and local anesthesia is administered to numb the site.
-
Incision: A small cut is made over the cyst.
-
Removal: The entire cyst, including its capsule, is carefully excised to minimize the risk of recurrence.
-
Closure: The incision is closed with sutures, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Advantages:
-
Provides a definitive solution by removing the cyst and its capsule.
-
Minimizes the chance of recurrence.
Considerations:
-
Requires a sterile environment to reduce infection risk.
-
May result in a small scar.
Reference:
2. Needle Aspiration
Procedure:
-
Preparation: The area is cleaned, and local anesthesia is applied.
-
Aspiration: A needle is inserted into the cyst to withdraw its fluid content.
-
Post-procedure: A bandage is applied to the site.
Advantages:
-
Minimally invasive with a quick recovery time.
-
Suitable for cysts that are fluid-filled and not deeply embedded.
Considerations:
-
Does not remove the cyst wall, so there’s a higher chance of recurrence.
-
Not suitable for all types of cysts.
Reference:
3. Laser Removal
Procedure:
-
Preparation: The area is cleaned, and local anesthesia is applied.
-
Laser Application: A laser is used to make a small incision, vaporize the cyst contents, and remove the cyst wall.
-
Post-procedure: A dressing is applied, and healing is monitored.
Advantages:
-
Minimal scarring due to precise tissue removal.
-
Suitable for small, superficial cysts.
Considerations:
-
Not all cysts are amenable to laser treatment.
-
May require specialized equipment and expertise.
Reference:
4. Steroid Injections
Procedure:
-
Preparation: The area is cleaned, and local anesthesia is applied.
-
Injection: A corticosteroid is injected into the cyst to reduce inflammation and promote shrinkage.
-
Post-procedure: The site is monitored for any adverse reactions.
Advantages:
-
Non-invasive with minimal downtime.
-
Can reduce cyst size and alleviate symptoms.
Considerations:
-
May not completely eliminate the cyst.
-
Potential for side effects like skin thinning or discoloration.
Reference:
🩺 When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider if:
-
The lump or cyst grows in size.
-
It becomes painful, red, or inflamed.
-
There is a change in the appearance or texture of the lump.
-
The cyst interferes with movement or function.
A healthcare provider can assess the lump, determine its type, and recommend the most appropriate treatment option.
📚 Further Reading
For more detailed information on cyst removal procedures, consider the following resources:
Absolutely. Here’s a detailed and practical breakdown of treatment options for lumps and cysts, especially small, non-cancerous ones (like sebaceous, ganglion, or epidermoid cysts).
🩺 Treatment Options for Small Lumps or Cysts
1. 🔍 Watchful Waiting (Observation)
-
When it’s used: If the lump or cyst is small, painless, and not growing.
-
What it involves: Your doctor may recommend monitoring it over time.
-
Why: Many cysts are harmless and may go away on their own.
-
Risks: It could grow, become painful, or get infected later.
2. 💉 Needle Aspiration
-
When used: For fluid-filled cysts (like ganglion or breast cysts).
-
Procedure:
-
Local anesthetic is applied.
-
A sterile needle is used to draw out the fluid.
-
-
Pros: Quick, minimal discomfort.
-
Cons: Cyst may come back since the sac (wall) isn’t removed.
Example: Ganglion cyst in the wrist.
3. 🩺 Steroid Injection
-
When used: To reduce inflammation in cysts or small inflamed lumps.
-
How it works: A corticosteroid is injected directly into the cyst or surrounding tissue.
-
Pros: Non-surgical, reduces swelling or recurrence.
-
Cons: Doesn’t remove the cyst or lump entirely.
4. 🔪 Surgical Excision (Minor Surgery)
-
When used: Best option if the lump is:
-
Painful
-
Getting larger
-
Repeatedly infected
-
Cosmetically concerning
-
-
Procedure:
-
Local anesthesia
-
A small cut is made to remove the lump and the entire cyst sac
-
Area is stitched and bandaged
-
-
Recovery: 7–10 days; stitches may need removal
-
Pros: Most effective, low recurrence rate
-
Cons: Small scar, mild post-op care needed
Example: Sebaceous cyst on the back or scalp.
5. 🔥 Laser Removal
-
Used for: Small, visible cysts or lumps (especially cosmetic areas)
-
How it works: A laser is used to create a small opening, vaporize the cyst content, and remove it.
-
Pros: Minimal scarring, precise
-
Cons: More expensive, not widely available
6. ❄️ Cryotherapy (Freezing)
-
Used for: Very small superficial cysts or skin growths
-
How it works: Liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and destroy tissue
-
Pros: Quick, no cutting
-
Cons: Can cause skin discoloration or recurrence
7. 💊 Antibiotics (if infected)
-
When used: If the lump is infected, red, hot, or draining pus.
-
Treatment: Oral or topical antibiotics to clear the infection
-
Note: Antibiotics alone won’t remove the cyst
🧾 Treatment Comparison Table
| Treatment Option | Invasive? | Removes Entire Cyst? | Recurrence Risk | Scarring? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | No | No | Possible | No |
| Needle Aspiration | No | No | High | No |
| Steroid Injection | No | No | Medium | No |
| Surgical Excision | Yes | Yes | Low | Yes (minor) |
| Laser Removal | Mild | Yes | Low | Minimal |
| Cryotherapy | No | Yes (small cysts) | Medium | Slight |
| Antibiotics (if infected) | No | No | N/A | No |